How to create an AI agent from scratch

Summary:
If you’ve ever wondered how to create an AI agent from scratch, the kind that automates tasks, converses intelligently, or makes strategic decisions, you’re not alone.
Entrepreneurs and solopreneurs worldwide are rapidly exploring AI agents to supercharge productivity, reduce costs, and scale operations.
An AI agent isn’t just a chatbot; it’s a digital autonomous assistant capable of perceiving its environment, reasoning through data, and taking meaningful actions toward defined goals.
From automating marketing workflows to personalizing patient care, AI agents are reshaping how we work, learn, and innovate.
This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about what AI agents are, how they work, and most importantly, how to build one from the ground up.
Key Takeaways
-
- AI agents are autonomous, intelligent systems that perceive, decide, and act toward defined goals.
- Entrepreneurs and solopreneurs can build agents to automate tasks, enhance decisions, and scale operations affordably.
- Building one involves defining goals, selecting architectures, coding perception–decision–action modules, integrating APIs, and iterating with feedback.
- The best agents combine reasoning (ReAct), memory (RAG), and ethics (alignment) for trustworthy autonomy.
- In business, education, and healthcare, they’re not replacing humans but amplifying them, freeing us to focus on creativity and connection.
What Are AI Agents?
An AI agent is a software entity that can observe its environment, process information, and act autonomously to achieve specific objectives.
These agents can operate in digital systems, physical robots, or hybrid setups that blend both.
AI agents are typically built using one of several agent architectures:
- Reactive agents: respond directly to stimuli (e.g., a customer support chatbot).
- Deliberative agents: reason and plan using models of the world.
- Hybrid agents: combine both reactivity and reasoning.
- BDI agents (Belief-Desire-Intention): simulate human-like decision processes.
At their core, AI agents follow a loop known as the perceive-think-act cycle:
- Perception: sense the environment or user input.
- Decision-making: reason or predict using machine learning or rules.
- Action: execute via APIs, code, or real-world devices.
Common frameworks like LangChain, ReAct, or AutoGPT enable developers to chain together tools, APIs, and prompts into autonomous workflows.

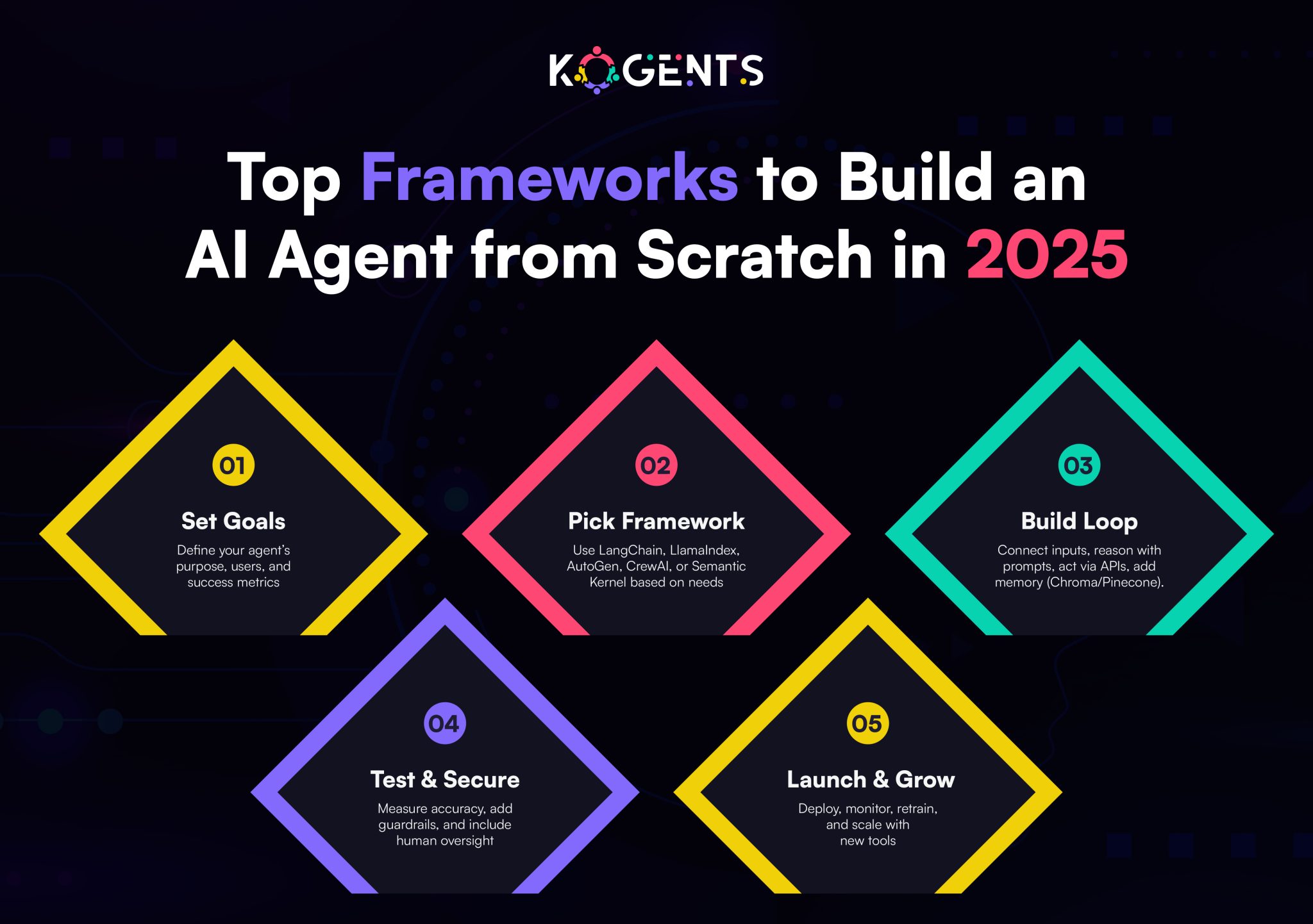
How to Create an AI Agent from Scratch
Creating an AI agent from scratch is less about writing lines of code and more about designing a thinking system that can understand, decide, and act.
The process begins long before development, with strategic clarity, behavioral modeling, and a deep understanding of your goals.
Here’s how to conceptualize, build, and refine an autonomous agent step by step.
1. Define the Agent’s Mission and Identity
Every powerful AI agent begins with a clear purpose.
Ask: What problem will this agent solve, and for whom?
This purpose defines its “mission statement”: whether it’s a business analyst, virtual assistant, or healthcare companion.
Entrepreneurs should define their agent as if hiring an employee: what role, responsibilities, and outcomes do you expect?
Once the purpose is defined, outline its personality and tone. Should your agent be professional and analytical, or empathetic and conversational?
This design step aligns the agent’s voice and reasoning style with your brand identity or user expectations.
In healthcare or mental health, for instance, warmth and trustworthiness are essential; in business analytics, precision and clarity matter most.
2. Map the Environment and Interactions
An agent’s world is its environment, the space it observes, interprets, and acts within.
This could be a business dashboard, a patient data system, or a client interaction platform.
- Defining this environment helps you visualize how the agent perceives information.
- Next, outline the inputs and outputs. Inputs might be customer questions, data sets, or user feedback.
- Outputs could include reports, actions, or decisions.
Learn It: This clarity ensures that your agent has the right “senses” and “tools” to operate meaningfully within your ecosystem.
3. Design the Cognitive Process: Driver the Thinking Engine
At the heart of every agent lies its cognitive process, how it interprets information, reasons through uncertainty, and takes action.
Conceptually, this follows the perception → reasoning → action loop.
-
- Perception: How does your agent gather and interpret signals from its environment? (e.g., text, user inputs, business data).
- Reasoning: How does it evaluate options, prioritize goals, and make decisions?
- Action: What can it actually do, respond, recommend, execute, or collaborate?
Strategic Insight: Think of this like training a team member: you’re teaching your AI how to notice what matters, think critically, and follow through responsibly.
4. Build the Behavioral Logic and Feedback Loops
To create one from scratch, you must define the feedback mechanisms that help it learn and evolve.
Imagine your AI agent as a digital apprentice: it performs tasks, receives feedback, and gradually refines its performance.
This could be user satisfaction ratings, business KPIs, or outcome accuracy.
When feedback is continuous, the agent’s behavior becomes more adaptive and aligned with your goals.
Entrepreneurs can also set reward signals, not in a coding sense, but strategically.
For example:
- Reward = successful client engagement.
- Penalty = unresolved task or incorrect outcome.
Key Note: Over time, this conceptual reinforcement process helps your agent “understand” what success looks like in your business.
5. Create Its Memory and Identity Continuity
To feel intelligent, it must remember context, previous decisions, and user preferences. Conceptually, this means designing short-term and long-term memory layers:
- Short-term memory allows your agent to hold recent interactions and maintain coherent conversations.
- Long-term memory helps it recognize patterns, preferences, and historical outcomes.
6. Align with Ethics, Trust, and Human Oversight
Before deploying, define your ethical guardrails. What should your agent never do? What human review processes are necessary?
Trust and transparency are the cornerstones of sustainable AI use, especially in healthcare or finance.
Every agent must be designed with alignment principles: fairness, explainability, and respect for privacy.
For solopreneurs, this might mean ensuring client data is never shared without consent.
For healthcare providers, it means building agents that support, not replace, professional judgment.
Key Highlight: This step transforms your agent from an automation tool into a trustworthy collaborator.
7. Pilot, Measure, and Evolve
- Finally, launch your agent in a controlled pilot environment.
- Measure how it performs in real-world conditions.
- Observe how users interact with it. Identify where it shines and where it struggles.
- Agents thrive in iterative cycles; analyze feedback, refine reasoning, and evolve their “mindset.”
Note: Entrepreneurs should treat this phase as ongoing mentorship, where their agent continues learning from results, patterns, and experiences.
Why Entrepreneurs & Solopreneurs Need AI Agents?
AI agents offer a way to clone their decision-making processes, enabling growth without burnout.
1. 24/7 Productivity
- AI agents don’t sleep.
- They manage leads, schedule posts, and reply to inquiries even while you rest.
- Solopreneurs can offload repetitive tasks and focus on creativity and strategy.
2. Scalable Operations
Entrepreneurs can deploy autonomous AI agents to handle parallel workflows, customer support, data analytics, or proposal generation, much like the solutions offered by the best agentic AI company for startups and growing teams.
3. Smarter Decision-Making
With data-driven insights, AI agents can evaluate KPIs, perform forecasting, and recommend actions using real-time analytics.
4. Personalized Experiences
Agents can tailor customer engagement by learning from behavior data, a competitive advantage for small businesses that want to deliver big-brand personalization.
5. Lower Costs
AI agents reduce overheads, with no salaries, benefits, or training costs, while maintaining consistent quality.
Pro Tip: Pair an AI business agent (for operations) with a creative agent (for content generation). Together, they create a self-sustaining business engine.
Core Features of Modern AI Agents
Modern AI agent architecture combines modular intelligence with adaptive learning. Key features include:
1. Context Awareness
Agents use retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) and vector search to recall prior interactions and maintain long-term memory.
2. Reasoning & Planning
Leveraging frameworks like ReAct (Reason + Act), agents can plan step-by-step actions, essential for complex workflows like financial analysis or treatment planning.
3. Multi-Tool Integration
Agents invoke APIs, databases, and cloud tools autonomously, transforming from static models to dynamic software operators.
4. Memory Systems
Long-term, episodic, and working memory modules allow context persistence and meta-reasoning.
Example: an agent can “remember” previous user goals and resume work later.
5. Safety & Alignment
Built-in ethical guardrails, sandboxed environments, and logging ensure compliance and transparency, crucial for healthcare or finance sectors.
6. Human-in-the-Loop (HITL)
AI agents incorporate manual override options, enabling human review for high-stakes decisions.
7. Learning Capabilities
Using reinforcement learning or fine-tuning, agents continuously improve via feedback loops and self-evaluation.
Together, these features enable autonomous, trustworthy, and adaptive behavior, bringing us closer to agentic AI — systems capable not just of executing commands but of understanding goals and strategically achieving them.
Benefits of AI Agents
1. Efficiency and Automation
AI agents automate repetitive tasks, ensuring consistency and freeing human capital for higher-order thinking.
2. Enhanced Decision-Making
Agents synthesize data into actionable insights, analyzing sales trends, patient outcomes, or user engagement metrics.
3. Personalization at Scale
With adaptive learning, AI agents deliver tailored user experiences, from personalized education modules to individualized treatment recommendations.
4. Cost-Effective Scalability
Building once, deploying infinitely, agents can serve thousands of users without proportional cost increases.
5. 24/7 Availability
They provide round-the-clock support, critical in healthcare, global business, and mental wellness.
6. Reduced Human Error
Machine consistency ensures higher accuracy in tasks like data entry, analysis, and compliance tracking.
7. Continuous Learning
Through reinforcement learning, agents improve based on feedback, ensuring better alignment with user goals.
Example: A small business using a sales AI agent reports a 40% boost in conversion rates due to smarter lead prioritization and personalized outreach.
Pro Tip: Integrate your agent into CRM, analytics, and social platforms to achieve end-to-end automation and holistic visibility.
Challenges & Limitations
While powerful, building an AI agent from scratch poses key challenges:
1. Data Dependency
- Agents require quality, labeled data to perform effectively.
- Insufficient or biased data can lead to poor decisions.
2. Ethical & Safety Concerns
- Unmonitored agents risk bias, hallucination, or unsafe actions.
- Implement alignment checks and human-in-the-loop validation.
3. Complexity of Integration
AI integration for legacy systems, multiple APIs, and maintaining context persistence requires robust agent orchestration and debugging.
4. Cost of Development
Although frameworks are open-source, training, storage, and compute can be expensive for small operators.
5. Evaluation & Transparency
- Unlike rule-based systems, agent reasoning can be opaque.
- Logging, explainability, and audit trails mitigate this.
6. Security Risks
- API misuse or prompt injection attacks can compromise systems.
- Sandbox environments and permission hierarchies are essential.
7. Over-Autonomy
- Fully autonomous behavior without control mechanisms can create trust issues.
- Implement permission boundaries and override switches.
Expert Insight: Joy Buolamwini’s Algorithmic Justice League highlights that fairness, bias detection, and ethical validation are not optional; they’re integral to sustainable AI.
AI Agents vs Other Tools
| Feature / Aspect | AI Agents | Chatbots | Automation Tools (Zapier, IFTTT) | Traditional Software |
| Autonomy | High – learns and acts independently | Low – responds to scripted inputs | Medium – rule-based | Low – static |
| Learning Ability | Yes (reinforcement learning, RAG) | Limited | None | None |
| Context Awareness | Deep, persistent memory | Minimal | Stateless | Fixed |
| Decision-Making | Dynamic reasoning and planning | Predefined responses | Conditional logic only | Manual setup |
| Adaptability | Self-improving over time | Static | Rigid | Requires manual updates |
| Integration Scope | APIs, databases, tools, sensors | Messaging apps | Limited web apps | OS or platform only |
| Best Use Case | Intelligent operations, strategy, insight | Customer chat support | Workflow automation | Standard processes |
| Example Frameworks | LangChain, AutoGPT, BabyAGI | Dialogflow, ManyChat | Zapier, Make | ERP, CRM systems |
Future of AI Agents
The future belongs to agentic ecosystems, interconnected networks of specialized AI agents that collaborate like digital teams.
According to recent arXiv papers (e.g., Cognitive Kernel-Pro, ThinkTank Framework 2025), we’re entering an era of multi-agent orchestration where AI agents negotiate, cooperate, and delegate tasks seamlessly.
Expect innovations in:
- Autonomous marketplaces — where agents transact and barter data.
- Verified identity standards like AgentFacts (KYA standard) ensure agent trust and accountability.
- Agentic AI certifications from institutions like MIT and NVIDIA — professionalizing agent design and AI governance and compliance.
| For entrepreneurs and solopreneurs, this means greater access to plug-and-play AI employees, marketing agents, analytics agents, and even finance advisors.
As LLMs become multimodal, agents will interpret voice, video, and sensors, bridging digital and physical realities. |
Case Study Spotlight
1. Business
A SaaS startup built a sales AI agent using LangChain and GPT-4. It qualified leads via email, integrated with HubSpot, and automated follow-ups.
Result: 40% sales increase, 60% fewer manual hours.
2. Healthcare
A clinic deployed an AI triage agent integrated with EHR. It monitored patient vitals, predicted risk using RL models, and alerted doctors proactively, improving diagnostic speed by 35%.
3. Mental Health
An online therapy platform used a BDI-based conversational agent to deliver CBT sessions. Clients reported a 25% improvement in stress management and engagement.
4. Education
A university integrated an AI tutoring agent powered by RAG. It provided real-time help for students, cutting dropout rates by 20%.
5. Learning & Self-Development
A solopreneur built a personal growth AI mentor that tracked progress across skills, set reminders, and curated courses.
Result: More consistent learning and measurable ROI on time spent.
Conclusion
Knowing how to create an AI agent from scratch isn’t science fiction; it’s a strategic imperative for modern entrepreneurs.
As agentic AI evolves, those who learn to design and deploy their own agents will hold a decisive advantage in automation, insight, and innovation.
You now know the core steps: define your purpose, design architecture, integrate APIs, and enable continuous learning.
Whether you’re running a one-person business or managing a digital clinic, the potential is limitless when you combine AI autonomy with human vision.
See how Kogents AI does it for you and get in touch with us by calling us at +1 (267) 248-9454 or dropping an email at info@kogents.ai.
FAQs
What is the easiest way to start building an AI agent?
Begin with open-source frameworks like LangChain or AutoGPT. They simplify tool integration and reasoning workflows.
Can I create an AI agent without coding?
Yes. Low-code platforms like Flowise or Pipedream let you drag-and-drop logic for agentic automation.
Which programming language is best for AI agents?
Python, due to its mature AI ecosystem (TensorFlow, PyTorch, LangChain).
How much does it cost to build an AI agent?
Basic prototypes can start under $50/month using APIs. Enterprise agents with RL training cost significantly more.
What’s the difference between a chatbot and an AI agent?
Chatbots respond; AI agents reason, plan, and act autonomously.
Can AI agents work together?
Yes. Multi-agent systems (MAS) enable collaboration, negotiation, and parallel task execution.

Kogents AI builds intelligent agents for healthcare, education, and enterprises, delivering secure, scalable solutions that streamline workflows and boost efficiency.